Eczema
What are the causes of eczema?
Many factors can contribute to eczema, including an interaction between your environment and your genes. When an irritant or an allergen from outside or inside the body “switches on” the immune system, it produces inflammation, or a flare-up, on the surface of the skin. This inflammation causes the symptoms common to most types of eczema. There is also a potential genetic component to eczema that includes a protein called “filaggrin” that helps maintain moisture in your skin; a filaggrin deficiency can lead to drier, itchier skin.
Many common household items are also potential environmental irritants and can cause allergic reactions leading to an eczema flare. Additional common triggers of eczema may include:
- extended exposure to dry air, extreme heat or cold
- some types of soap, shampoo, bubble bath, body wash, facial cleansers
- laundry detergents and fabric softeners with chemical additives
- certain fabrics like wool or polyester in clothing and sheets
- surface cleaners and disinfectants
- natural liquids like the juice from fruit, vegetables and meats
- fragrances in candles
- metals, especially nickel, in jewelry or utensils
- formaldehyde, which is found in household disinfectants, some vaccines, glues and adhesives
- isothiazolinone, an antibacterial found in personal care products like baby wipes
- cocamidopropyl betaine, which is used to thicken shampoos and lotions
- paraphenylene-diamine, which is used in leather dyes and temporary tattoos
Emotional stress can also trigger an eczema flare-up, but it’s not exactly known why. Some people’s eczema symptoms and flare-ups get worse when they’re feeling “stressed.” Others may become stressed, just knowing they have eczema, and this can make their skin flare up.
What are the symptoms of eczema?
The most important thing to remember is that eczema and its symptoms are different for everyone. Every individual’s skin care routine will also impact the affected areas of the skin differently. Your eczema may not look the same on you as it does on another adult or on your child. Different types of eczema may even appear in different affected areas of the body at different times. Some people mistake symptoms of psoriasis for eczema, although the two conditions are different.
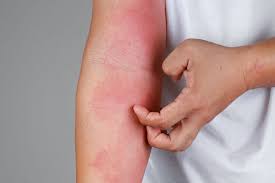
Eczema almost always includes itchy skin. The scientific term for itch is “pruritus.” For many people, the itch can range from mild to moderate. Sometimes the itch gets so bad that people scratch it until it bleeds. This is called the “itch-scratch cycle.”
Symptoms of eczema often include:
- Itch;
- Dry, sensitive skin;
- Inflamed, discolored skin;
- Rough, leathery or scaly skin, appearing as scaly patches;
- Oozing or crusting;
- Areas of swelling.
You might have all of these symptoms of eczema or only just a few. You might have some flare-ups or your symptoms could go away entirely. Eczema can appear red in lighter skin, whereas people of color may experience eczema as ashen skin, grey skin, darker brown or purple in color. Black Americans are more likely to report severe symptoms associated with eczema.
The best way to find out if you have eczema is to consult with a healthcare provider, such as a dermatologist who has experience diagnosing and treating eczema.
Is there a cure for eczema?
Treatment is available...Come see the Dermatologist for specific treatment.


